Innovative Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable batteries provide a tangible means for non-specialists to experience the abstract concept of energy within physical space. Among them, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are the most prevalent, representing a landmark achievement recognized by the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. These systems have become essential in powering portable electronic devices and electric vehicles, serving as a cornerstone of contemporary energy technologies.
However, LIBs face fundamental limitations in terms of energy density, resource availability, and safety. To address these challenges, the development of next-generation energy storage devices based on alternative energy conversion principles is imperative.
Emerging battery systems that utilize the transfer of multivalent cations or anions between electrodes offer promising pathways to surpass the performance of LIBs. Despite their potential, these systems encounter significant technical obstacles, including limited ion conductivity and poor interfacial compatibility with electrode materials.
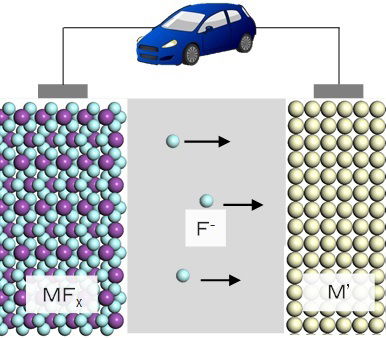
To overcome these barriers, our research focuses on the design of novel electrode and electrolyte materials, alongside comprehensive analyses of their physical properties and interfacial reaction mechanisms. One such target is the fluoride shuttle battery, a rechargeable system that operates via the reversible transport of fluoride ions. This battery architecture holds promise for achieving remarkably high energy densities. Our approach involves the development of advanced fluoride-conducting electrolytes and compatible electrode materials, coupled with in-depth studies of the electrochemical processes occurring within the system, with the ultimate goal of establishing rational design principles for future high-performance energy storage technologies.
エネルギーという非専門家には理解し難い概念を実空間で体感できる媒体として蓄電池がある。
蓄電池の中で現在最も代表的なものとして、リチウムイオン電池がある。2019年のノーベル化学賞の受賞対象となったリチウムイオン電池は、小型デバイスから自動車など広く用いられ、現代のエネルギー技術において中核的な役割を果たしている。一方では、リチウムイオン電池にも限界があり、それを超える新たなエネルギー変換技術に基づくデバイスの開発が期待されている。
多価イオンやアニオンの電極間の移動を利用した蓄電デバイスは、リチウムイオン電池の性能を超える可能性を持っており、その発展が期待されているが、イオン伝導や電極との反応性など多くの課題がある。
これらの課題を克服するために、新たに電極や電解液を開発し、さらに材料物性や反応機構を解析することで、新しい蓄電デバイスの設計指針を確立する。例えば、フッ化物イオンの移動を用いた蓄電池であるフッ化物イオンシャトル二次電池は、極めて高いエネルギー密度が期待できる電池系であり、電極と電解液を開発し、その反応機構を解析する。
Representative papers
Chem. Phys. Lett. 755, 137785 (2020).
セラミックス 54, 637 (2020).
J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 10246 (2019).
J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, A3702 (2017).